Digitalization
Digitalization as a major enabler
Digitalization is a challenge that affects everyone: companies, the state and society as a whole. There are major differences in the state of digitalization in the economy. The information and communications industry can be seen as a pioneer as well as a driver of digitalization in other industries. Vehicle manufacturing, mechanical engineering and the electrical industry are already digitalized to an above-average extent. There, a majority of companies are aware of the relevance of digitalization, says the Institute of the German Economy.

In addition to legal gray areas and a lack of experts, the main obstacles to digitalization include a lack of clarity about the benefits associated with data-driven business models, for example. The business environment, characterized in Germany for example by a digital infrastructure that is often still unsatisfactory and e-government that is underdeveloped by international standards, is also hampering further digitalization.
The challenge is: digitalization knows no boundaries. For German or European companies with international operations in particular, it is therefore of great relevance how digitalization is handled abroad. The EU, the U.S., and China have different approaches here; moreover, digital platforms from the U.S. and China are already increasing competitive pressure and the dynamics of markets. It is therefore all the more important to move forward at an increased pace in the digitalization of companies and in the development of data-based business models. Here, the B2B sector in particular offers great entrepreneurial potential, and this is where ABP Induction is particularly active, developing technical solutions to reduce emissions and consumption in energy-intensive steel mill and foundry processes, increase plant output and improve plant availability. Five years ago, ABP Induction began a massive diversification of its offering in this area and established a digital business unit. Today, ABP offers an extensive portfolio of digital solutions that are indispensable to metalworking companies if they are to fully exploit all potential in terms of decarbonization and energy efficiency. ABP Induction has developed a digitalization strategy for this, which is based on five pillars and takes into account all three aspects of sustainability: ecological, economic and social drivers. These five pillars reflect solution paths that companies must follow in order to remain competitive in the future and to be able to provide answers to the pressing questions that emerge from these megatrends.
Open platform economy: It is clear that answers to today's most pressing questions can only be found by working together. Focus is on cooperation, across industries and with the participation of all forms of enterprise, from startups and SMEs to large corporations and academic institutions. Solutions must function independently of platforms and manufacturers, there must be open access to be able to work out solutions. To this end, ABP Induction has developed myABP, a central digital platform for all products and machines, which is independent of manufacturers.
Book demo session at the fair now
Digital data sovereignty: Data is the most important asset in digital processes. No analysis and no digital processes for saving energy, controlling processes and optimizing plants can be achieved without data. It goes without saying for ABP Induction that data sovereignty will remain with the plant operator. This operational asset must be protected. ABP Induction will only access this data if the operator consents and actively provides data for the purpose of proposing optimization or solutions using their own expertise. This is the point where all knowledge-intensive information converges and can be collected, evaluated and analyzed so that conclusions can be drawn and measures can be taken in production, maintenance and servicing.
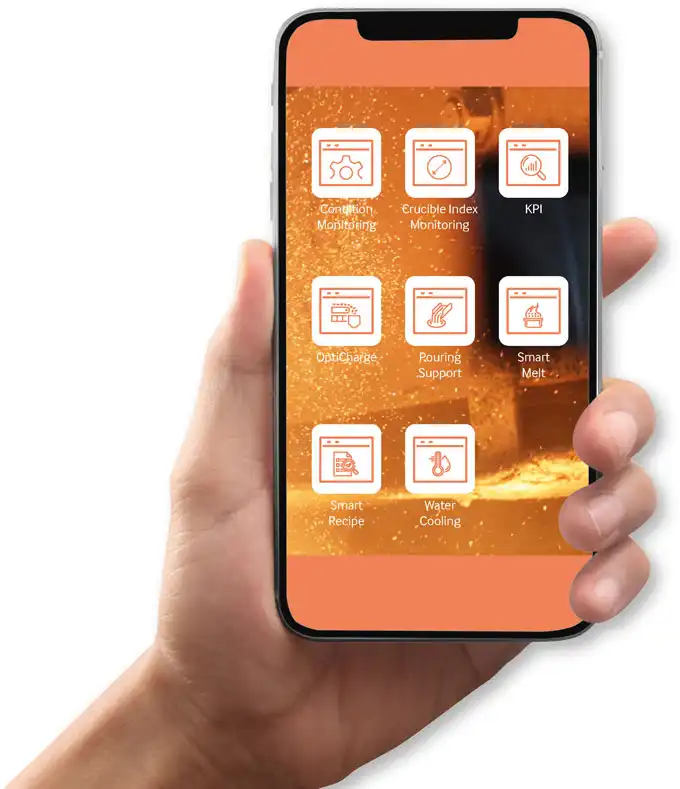
Digital intelligent processes: ABP Intelligence is a comprehensive portfolio of smart apps for condition monitoring and plant control. They are available on an Edge PC and in their entirety function as a smartphone for the foundry, for example with an app for digital information and maintenance assistance, for documentation, production data, service reports and much more. ABP Intelligence Apps can be installed completely locally and do not need access to the cloud: data is not uploaded to the cloud.
ABP Induction works together with well-known partners such as the Norican Group: “ABP and Norican are both highly motivated to help digitalise the foundry industry, and linkages like this between different suppliers are vital to support completely connected digital eco-systems. Without them, it will be impossible for foundries to extract the full value from their data,” says Nina Rasmussen, Senior Vice President, Head of Monitizer, Norican Group on the linking of ABP and Norican.
Digital services: Location and time-independent support for repairs and maintenance anytime it is needed - this is what the augmented reality solution "ABP Expert on Demand" was developed for. ABP experts can deliver support worldwide at any time and guide technicians at the plants on site to perform the relevant steps for maintenance and servicing. This is based on the "follow-the-sun" principle: experts are available in most regions of the world to provide support at any time so that, in the event of an incident, plants are idle for as short a time as possible. For this purpose, companies can view relevant spare parts via the web store and, if required, select them directly for an order - the processing is carried out by the ABP service department.
Digital training: To meet the challenges of demographic change, digitalization strategy also encompasses employee-related offerings. These offerings make it possible to expand qualifications. This can be done in classic collaboration tools such as Microsoft Teams & Co., or in the virtual training environment ABP Virtual Classroom - for example, when it comes to training safety-relevant work steps in operation and maintenance that would not be trainable in reality - on a digital twin. Digitization makes expert or practical knowledge accessible - also relevant for onboarding of new employees. Operations run efficiently, employees are trained more effectively, and can be deployed productively more quickly.


